The combustion of octane is a common reaction in automobile engines.
1) 2 C8H18 (l) + 25 O2 (g) → 16 CO2 (g) + 18 H2O (g) ΔH1 = -250 kJ/mole
2) 18 H2O (l) → 18 H2O (g) ΔH2 = 88 kJ/mole
Net Reaction:
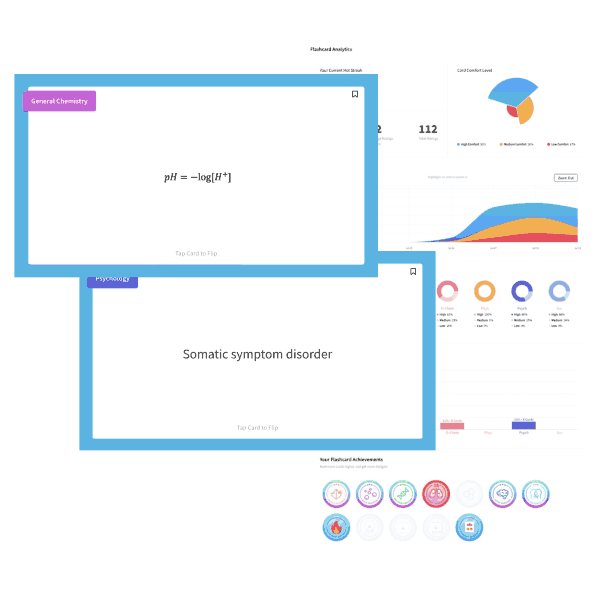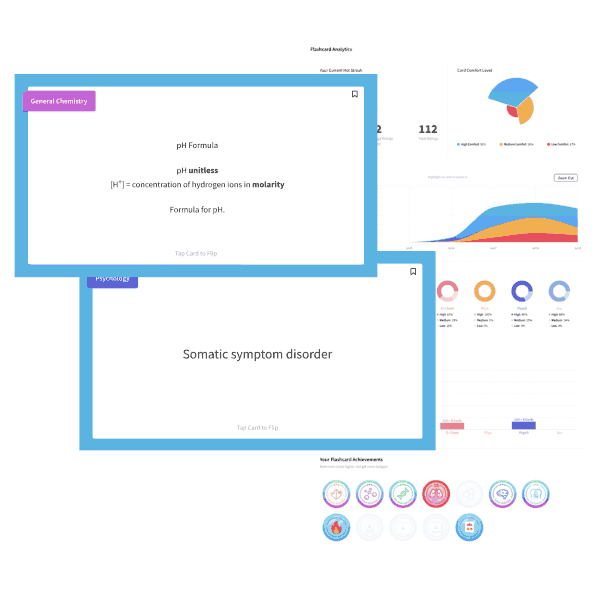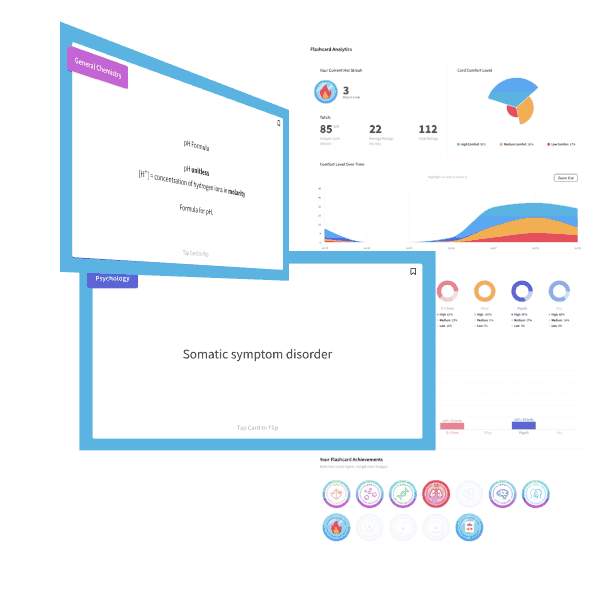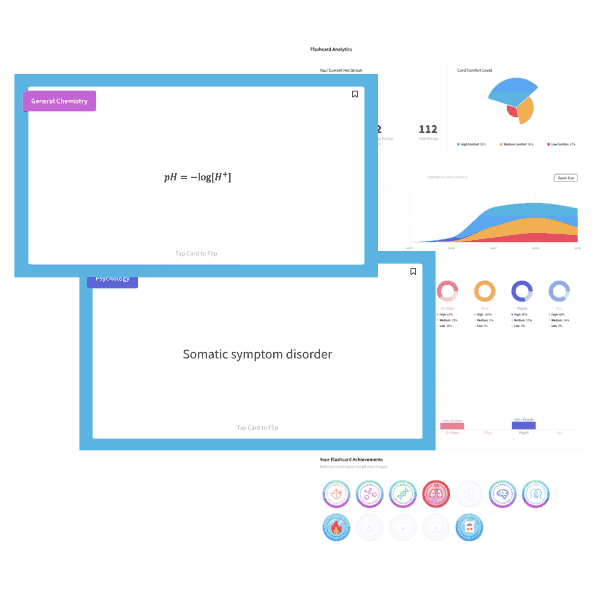
3) 2 C8H18 (l) + 25 O2 (g) → 16 CO2 (g) + 18 H2O (l) ΔH3 = ?
Given ΔH1 and ΔH2, what is ΔH3 for the net reaction above?
A. 162 kJ/mole
B. -162 kJ/mole
C. 338 kJ/mole
D. -338 kJ/mole
Click for Explanation
This question asks you to determine the change in enthalpy for a net reaction given the enthalpy change for two other reactions. Hess’s Law tells us that the sum of two reactions gives us the enthalpy change for the net reaction: ΔH1 + ΔH2 = ΔH3. Since the net reaction has H2O (l) as a product, reaction 2 must be reversed and the sign of the enthalpy change negated (-ΔH2). The sum of the reaction enthalpies for the net reaction is as follows:
ΔH3 = ΔH1 + (-ΔH2)
ΔH3 = -250 kJ/mole + (-88 kJ/mole)
ΔH3 = -338 kJ/mole
Therefore, the change in enthalpy (ΔH3) for the net reaction above is -338 kJ/mole, or answer choice D. Furthermore, the combustion of a fuel is a highly exothermic process, making answer choices A and C incorrect.
Want more MCAT practice?
We’ve got options for every schedule and learning style!
From the best online MCAT course created by top instructors with 524+ MCAT scores to the most representative full-length practice exams and private tutoring, we can custom tailor your MCAT prep to your goals!
Not sure which option is right for you? Schedule a free MCAT consultation with an MCAT expert using the form below. No obligation, just expert advice.
MCAT is a registered trademark of the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC), which is not affiliated with Blueprint.
