Similarities in chemical behavior can be observed between elements within the same family in the periodic table. For instance, sodium and potassium react with oxygen to produce a metal oxide. Which of the following gives the balanced reaction for the oxidation of an alkali metal (M)?
- 2M(s) + O2(g) → 2MO(s)
- 4M(s) + O2(g) → 2M2O(s)
- 3M(s) + O2(g) → M3O2(s)
- M(s) + O2(g) → MO2(s)
Click for Explanation
Sodium and potassium are congeners found in the first column of the periodic table. They are included in the alkali metal family and exhibit similar chemical reactivity. In the presence of oxygen, alkali metals are oxidized. To form a complete octet, alkali metals lose one valence electron and take on their preferred oxidation state of +1. Oxygen, on the other hand, completes its octet by gaining two electrons to form an anion with a charge of -2. Thus, in the reaction above, two metal (M) atoms must each lose one electron in order for each oxygen atom to gain two electrons. Of the reactions above, B is the only choice where the metal (M) has a charge of +1 and oxygen had a charge of -2 with a 2:1 coefficient ratio of metal to oxygen. Thus, B is the correct answer for the oxidation of alkali metals.
Want more MCAT practice?
We’ve got options for every schedule and learning style!
From the best online MCAT course created by top instructors with 524+ MCAT scores to the most representative full-length practice exams and private tutoring, we can custom tailor your MCAT prep to your goals!
Not sure which option is right for you? Schedule a free MCAT consultation with an MCAT expert using the form below. No obligation, just expert advice.
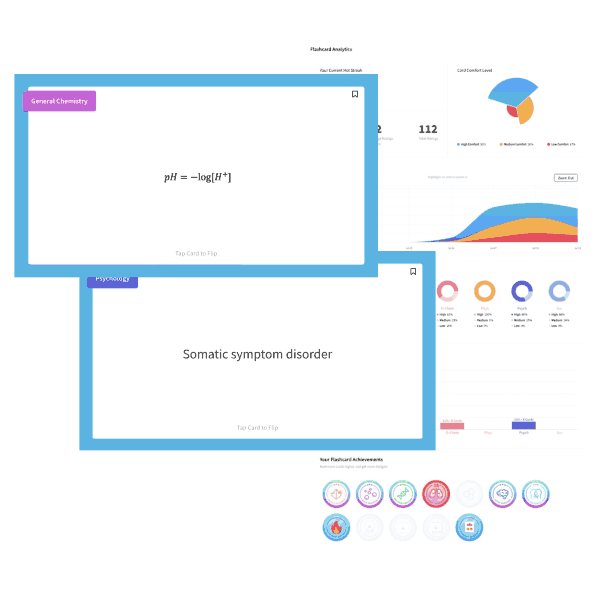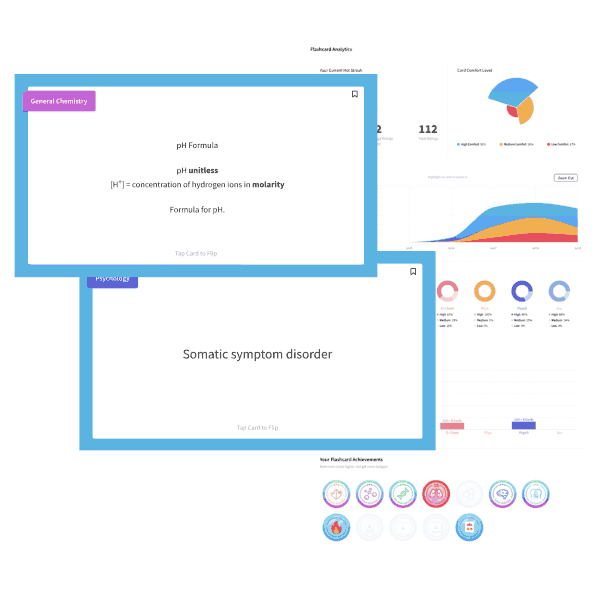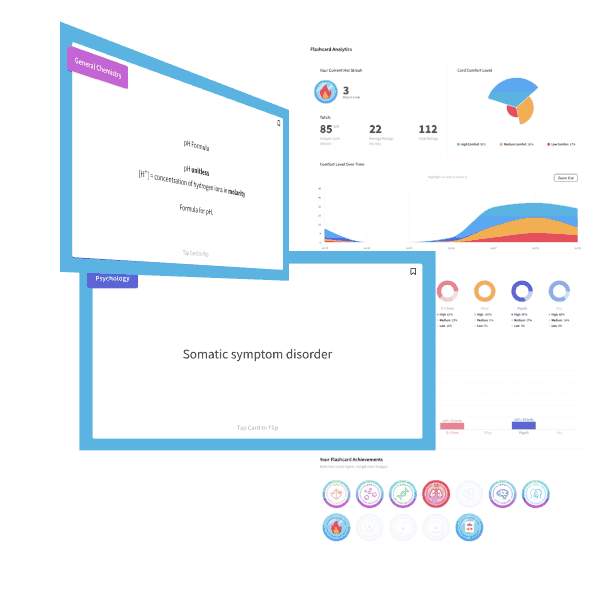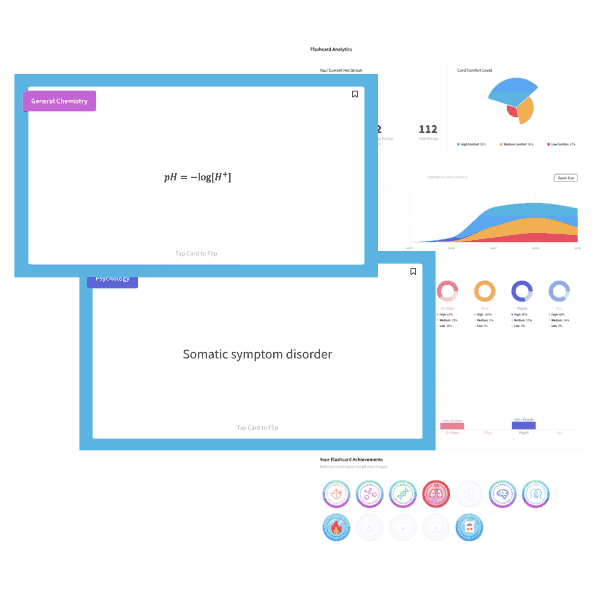
MCAT is a registered trademark of the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC), which is not affiliated with Blueprint.
