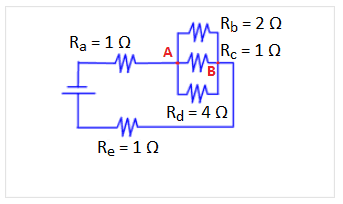
The voltage drop across Rd is 8 V. What is the current across Re?
A. 2 A
B. 8 A
C. 14 A
D. 32 A
Click for Explanation
This problem requires 3 electrical circuit concepts:
1) V = IR, which relates voltage, current, and resistance
2) The fact that the voltage drop across resistors in parallel is equal in each resistor
3) Kirchoff’s junction law, which states that the sum of currents entering a node equals the sum of currents leaving a node
The voltage drop is equivalent for each resistor between red nodes A and B. The voltage drop across Rd is given as 8 V, and therefore the voltage drop across resistors Rb and Rc is also 8 V. Using V = IR for each resistor, the current in resistor Rb = 4 A, Rc = 8 A, and Rd = 2A. Using Kirchoff’s current law at node B: 4 A + 8 A + 2 A = 14 A. The current leaving node B equals the current across Re because there are no other nodes in between.
A. 2 A, incorrect, this implies that the current across Rd = Re.
B. 8 A, incorrect, this implies that the current across Rd equals the voltage and the current across Re.
C. 14 A, correct.
D. 32 A, incorrect, this answer incorrectly assumes a voltage of 8 V across Re and then uses a false relationship VR = I.
Want more MCAT practice?
We’ve got options for every schedule and learning style!
From the best online MCAT course created by top instructors with 524+ MCAT scores to the most representative full-length practice exams and private tutoring, we can custom tailor your MCAT prep to your goals!
Not sure which option is right for you? Schedule a free MCAT consultation with an MCAT expert using the form below. No obligation, just expert advice.